Ankit Raj
Head of Growth at Rise In
May 19, 2024
Blockchain 101: A Beginner's Guide to the Technology Behind Web3
Demystifying the Building Blocks of Decentralized Applications
.png)
Blockchain technology is an advanced database mechanism that allows transparent information sharing within various industries network. It has emerged as a revolutionary force, reshaping industries and paving the way for the decentralized web, often knowns as Web3.In this tutorial , we’ll go through the fundamental concepts of blockchain and its importance in the context of Web3.
What is Blockchain?
It is a distributed database with growing lists of records(blocks) that are securely linked together via cryptographic hashing technology. Unlike traditional databases, which are centrally controlled, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, ensuring greater transparency and immutability.
Key Components of a Blockchain
1. Blocks: In blockchain, data is organized into blocks, each containing a set of transactions. These blocks are linked together in a chronological order, forming a chain.
- A block is simply a container for data — it groups data together. The “data” can be anything digital — an image, a book, property records, or a history of monetary transactions (i.e. a ledger).
2. Cryptography: Cryptographic techniques such as hashing and digital signatures are inherent to blockchain security. Hash functions ensure data integrity, while digital signatures authenticate transactions.
3. Consensus mechanisms: Consensus algorithms like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake govern how transactions are validated and added to the blockchain. These mechanisms ensure agreement among network participants.
4. Smart Contracts. They are self-executing contracts with predefined conditions written in code. They automate and enforce the terms of an agreement, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
How Blockchain works
The first concept in a blockchain is a block. And to understand a block , you’ll need to learn: Hashing. It is one of the key cryptographic concepts that the blockchain technology is built on.
A hash is a summary of the original data essentially.
- Bitcoin uses SHA(Secure Hash Algorithm) -256 hash. One input always generates the same hash, but it is impossible to predict the input back from the hash.
For instance an input like a name or an article will generate a specific hash, let’s for example imagine you have used the name “data” if you try to change even a single letter it shall change the hash generated to something else.
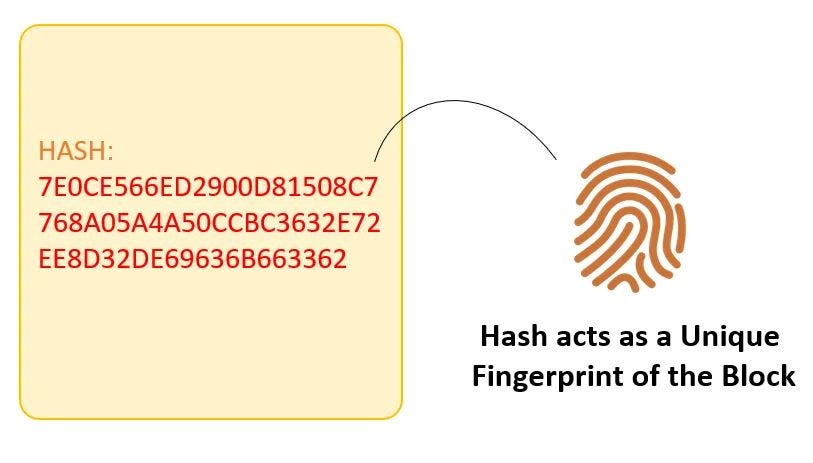
hash output example
💅Fun fact: SHA-256 was actually developed by the National Security Agency in the US.
Hashing enables us to efficiently compare whether data is changed. Many structures in the blockchain will be built using hashing. When we want to add new blocks, we just chain the new ones to the end of the previous one. This way we create consecutive dependencies between blocks.
Single Chains
Our goal is to build a system where individuals can add data and collectively agree which data is the “truth” without a central authority deciding it for them. They are connected to each other through hashing. Am sure you are wondering what “truth” means in this context, it is basically refers to the accuracy, integrity and immutability of information stored on the blockchain.
single chain blockchain
Distributed chains
A distributed system can have conflicting versions. In this distributed system, we need to introduce some mechanisms for the “true” blockchain to emerge.
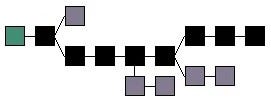
distributed chains
There are two fundamental, interdependent tweaks we shall implement. We will make it faster to add blocks that are truthful and we will then assume the longest chain is the most truthful chain for the network to use. To make sure that the “true” blocks will be added faster, we can introduce a few dynamics to the blockchain.
a) First we will make it time consuming to add new blocks by forcing computers to solve a difficult puzzle to create a new block.
b) Second multiple computers are to work on a puzzle. If more computers try to solve the puzzle simultaneously and the first one to solve the puzzle shares the solution with the others. This makes it fast to solve the puzzles since the others just have to confirm the input hence moving to the next puzzles. So the version of blocks that more computers work on gets added faster.
As a result, whatever the majority of the computers in the network agree on is added faster and the longest chain contains these blocks. If the majority of computers working on the blockchain are honest and they’re not organized to change the data, a bad actor will not be able to manipulate the data. They'll have no way to catch up with the speed of the longest blockchain and their blockchain will not be void. When a majority of computers(at least 51%) are coordinated and they manipulate a given data by solving puzzles faster and building a longer chain they create an alternate truth.
This is the only way to “hack” a blockchain also referred to as 51% attack. If the blockchain is long enough, its almost impossible to go back and change data in previous blocks. Since, then, the hash of the block changes, which requires changing hashes of all subsequent blocks.
The system we designed lets one single true blockchain emerge. Now let’s dig into the kind of puzzle typically used in blockchain. For our larger system to work as we described , this puzzle has to be something that:
1) Inevitably takes time and energy to solve.
2) Let’s multiple computers collaborate.
3) Is easy for others to confirm when it is solved.
Blockchain Puzzle
Here is the puzzle that blockchains typically use: “What additional series of numbers can I add to the blocks, so that the hash I generate for the whole block with X number of zeros?” ( let’s say for example 4 zeros). It’s impossible to guess the input of a hash calculation, there is no straightforward way for a computer to calculate these additional numbers which is called nonce - a number used only once.
It’s time consuming to do it, if more computers try to solve the same puzzle they can guess the right nonce faster. Since a hash can be calculated instantaneously, once found it is easy for other computers to confirm the puzzle is solved. When a puzzle for a new block is solved, that block can be added to the blockchain. For every additional number of zeros we require, the mining difficulty goes up exponentially. The Bitcoin network adjusts the mining difficulty in a way that takes around 10 minutes to make a block.
Hash rate is the number of hashes a miner can calculate per second. The higher the hash rate the more likely you are to validate a block. When hashing a 1mb block(Bitcoin block size) your hash rate is 5 hashes per second. In other words your computer can check 5 different nonce values for a block in 1 second.
Mining is adding a new block by finding its nonce value {It requires computers to do some work of solving the puzzle and show the proof of this work( the valid nonce) to add a new block}.
For computers to solve the puzzle and add a new block, they have to keep a copy of the entire blockchain. These computers are called nodes. That's where a concept called “ decentralization” comes in.
Conclusion
In summary, blockchain is designed to enable distributed, decentralized systems to agree on the same version of data. By breaking down data into blocks and chaining them together, blockchain facilitates transparent and secure information sharing across a network of nodes. Consensus mechanisms and cryptographic techniques ensure the accuracy, integrity, and immutability of data on the blockchain, making it a reliable and trusted technology for Web3 applications.